Image technology is advancing faster than ever, high definition (FullHD) has become a standard and the choice of which TV to buy is based on other factors, parameters and prices. As already done for computers, let’s see the things to know before buying a new TV.
Unfortunately, partly due to the commercial strategies of electronics manufacturers, it is difficult to understand if one technology is better than another. A TV may cost less but have a sharper picture than another which, according to the vendor, has superior technology. The consumer remains very confused in front of these indications which would seem to deny what is seen by eye.
This complete guide will show you in detail what are the differences between the various LED TVs on the market, so you can choose the best TV to put in the living room or kitchen, always getting the highest image quality.
READ ALSO -> New Smart TV and DVB-T2 to buy
New TV features
Before continuing, it is advisable to keep in mind the most important terms relating to the latest generation of TVs, to know the meaning of.
- Contrast ratio: Difference between white and bright colors with darker colors and black; The higher the ratio, the better the contrast.
- Refresh Rate: This item indicates how many times the screen “refreshes” the created image. The refresh rate is measured in hertz or cycles per second. The higher the refresh rate, the better the quality of moving images, with reduced blur and greater clarity. It starts from a minimum of 50 Hz up to even 1000 Hz.
- Pixel response time: Similar to the refresh rate, pixel response time is the number of milliseconds that individual pixels react to image changes. Response time refers to how quickly individual pixels change color from white to black, red or green. The lower the time, the better and fast moving images will be less blurry.
- Resolution: now all televisions on the market have a resolution of 1920 × 1080 (FullHD); those who want to spend less can still find and buy an HD Ready TV with a lower resolution, useful for televisions with a diagonal of less than 30 inches.
The listed features also change based on the TV model we are going to analyze and the type of panel present as a screen, which can make the difference between an average TV and a high-end TV.
TV LED
Classic TVs are labeled as LED TVs: these devices come with an LCD-type front screen but with a LED-based backlight, which therefore offers greater energy savings and longer life.
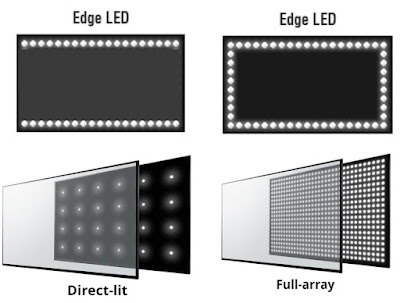
On LED TVs we find different methods to diffuse light, from the cheapest to the most expensive:
- Edge LED: Traditional system in which the LEDs are positioned along the edge of the screen and spread the light over the entire panel thanks to a system of prisms. The quality is good but halos of light are often evident due to some small imperfection in the diffusion of light.
- Direct-lit: With this system, the LEDs are positioned at the rear of the TV, thus creating well-defined areas of light. The diffusion of light is also helped in this case by the first ones but the image quality (and contrast) is higher, since in the case of black images the area of the TV that must reproduce the black is turned off.
- Full-Array: This advanced system provides direct lighting without a diffusion panel, with numerous LEDs positioned directly on the rear of the television. In this case, each LED provides light for a certain number of pixels: the lesser the quantity of pixels that a single LED illuminates, the higher the video quality (in particular the contrast). The ideal configuration is one pixel = one rear LED, but this solution is extremely expensive and rare (in fact we usually find LEDs that illuminate groups of pixels, usually from 5 to 10 pixels).
In any case, we will obtain a definitely higher quality than the classic LCD with lamp backlight panel, very popular until 2010 and quickly fallen into disuse.
A good Full-Array LED TV model we can consider is the Sony BRAVIA KE-65XH90P for € 1149.
TV QLED
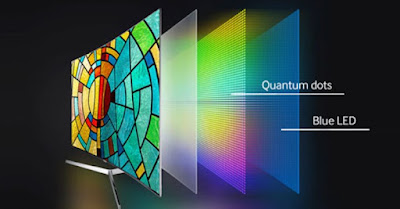
With this acronym we identify the televisions produced by Samsung, able to compete with the most advanced OLEDs. On these televisions we find an LCD panel, a blue LED backlight panel (usually Full-Array or Direct-lit) and an additional light diffusion panel (Quantum Dot), which offers a higher color rendering than traditional LED TV .
With this technological gimmick, Samsung has extended the life of LCD LEDs, managing to sell panels with a very high color rendering in any light condition. The evolution of this technology is known as mini-QLED or NanoQLED, where the Quantum dot panel presents even smaller quanta of light, improving contrast and color rendering.
Other manufacturers have also proposed solutions similar to QLED, just think of LG’s NanoCell, LG’s Qned and Sony’s Triluminos.
A good TV with QLED technology is the Samsung QLED TV QE50Q65AAUXZT for € 669.
READ ALSO: OLED or QLED: what is the best technology for new TVs?
TV OLED
The maximum evolution of TV panel technology is definitely OLED. With this technology, the backlight panel that has characterized all the LCD and LED TV models is no longer valid, since each pixel corresponds to a precise organic LED; the organic LED in question emits both light and the color of the pixel, significantly reducing the thickness of the television.
With this technology we will get a perfect black (high native contrast) and an excellent color rendering, at the expense of a lower brightness than the LED LCDs.
If we want to focus immediately on the highest TV technology we can buy the LG OLED55C14LB for € 1399.
READ ALSO: What is an OLED TV, advantages and differences with LED TVs.
Other types of TV screens
In addition to the types of TV panels seen above, it is also advisable to get to know the types that have now fallen into disuse closely, so as to be able to make a comparison:
- Standard LCD TVs: On these TVs the backlight panel consisted of high-energy lamps, which produced light for the front LCD panel. Disused due to the high energy consumption and the too imprecise light diffusion effect.
- Plasma TVs: Plasma screen TVs had good picture quality and contrast and worked by sending an electrical discharge onto an inert gas (usually neon or xenon), which generated a plasma suitable for exciting the front phosphors, thus emitting light for the actual image. These televisions consumed very much (even 200-300 Watts during use) and fell into disuse with the spread of LED TVs.
- Rear projection televisions (RPTVs): This type of TV is no longer found in shopping malls and is now only used for specific needs. It is an evolution of the cathode ray tube CRT, with a much thinner thickness and a much lower weight (inside they are almost empty). Rear projection TVs are recommended for those who need a very large screen, even 82 inches.
- 3D TVs: These TVs were very popular between 2007 and 2012, only to fall into disuse due to a lack of movies and channels that broadcast in 3D. Most of the time they were simple LCDs capable of splitting colors and reproducing 3D images. On the subject we can read our guide on the differences between active and passive 3D TV models with or without glasses.
In another article
READ ALSO: NanoCell vs. OLED: which TV screen looks best?
Smart TVs deserve a separate mention, which regardless of the type of panel allow you to connect to the Internet and take advantage of dedicated apps to access streaming services and online videos without having to use a computer.
Conclusions
Understanding which TV to buy depends a lot on your specific needs and use of the TV. For example, if you watch football matches and sports, we can focus on any modern TV that has a good image frequency (at least 100 Hz), while for those who often see movies the most logical choice is Full-Array LCDs, Direct-lit LCDs or OLEDs.
Those who often see digital terrestrial or Sky channels can also focus on QLEDs (and variants) or Direct-lit LCDs, which boast good value for money. Those who want to save money can focus with their eyes closed on the Edge LEDs, which consume very little and are seen fairly well on low viewing diagonals (such as 30 or 32 inches).
In another article I explained the various types of connectors and cables behind a TV.
If, on the other hand, we do not know which operating system to rely on Smart TVs, we can read our guide to the best Smart TVs by operating system: Samsung, Sony, LG, Panasonic.