The concept of tempo, inexorable in its universal nature, also takes on crucial importance in the field of information technology. In the digital world, time accuracy and synchronization are key to orchestrating processes, ensuring transaction security, recording events sequentially, and ensuring the correct functioning of networks and distributed systems. Time, from a simple abstract variable, becomes an indispensable element for the coherence and integrity of IT operations. So, in 1977, a computer engineer called Dave Mills proposed a protocol, NTP (Network Time Protocol), which would later become a standard, a true point of reference on a global scale.
What is NTP, how it works and what it is used for
NTP is a network protocol used for synchronize clocks of any device within a network. NTP’s main objective is to ensure a accurate timing and consistent across connected devices.
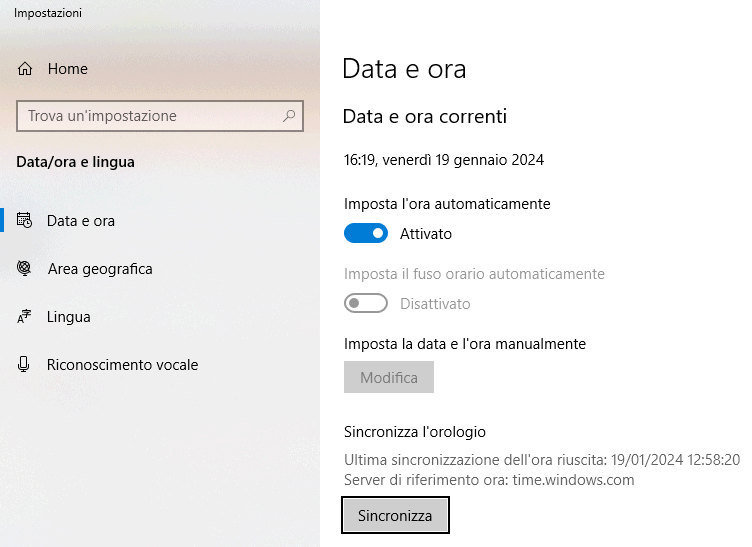
The battery backup used on many devices (not just desktop PCs and notebooks) allows the system clock to be kept active and updated even when the device is turned off. Even when this battery runs out, however, after starting the system, date and time they update automatically. This happens if and only if the machine is connected to the network and can exchange data with a server NTP reliable. The latter provides the correct date and current time with the best possible approximation.
Try writing Date and time in the Windows search box then choose Date and time settings. At Synchronize your watchyou will find the NTP server used by your system.
By opening the Windows Command Prompt (press Windows+R then type cmd), then by issuing the following instruction it is also possible to read the address of the NTP server in use:
reg query HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters /v NtpServer
The main functions of NTP include clock synchronization, management of time deviations (just think that 70 million years ago a year was made up of 372 days of 23 and a half hours each) and compensation for network transmission delays. NTP uses a hierarchical architecture: devices synchronize their clock with some NTP servers which, in turn, can synchronize with other even more precise servers, creating a reliable time reference chain.
How NTP was born and why clock synchronization is essential
Developed by David “Dave” L. Mills at the University of Delaware, NTP was presented in 1985, in the form of its first stable version. Since then, various versions have followed: the most updated and still current is NTPv4 (June 2010).
Mills, born in 1938, unfortunately left us on January 17, 2024. Now blind, due to glaucoma which manifested itself from an early age, the engineer is universally considered one of pioneers of the Internet. A few years ago Mills declared that the idea of NTP was the “his little fiefdom” because in the late 70s no one else was working there.
The role of NTP in communications
Anything but a “small fiefdom”! NTP’s invention turned out to be a real one cornerstone for everything that came after. Always maintain correct timeline of events is fundamental in computer science. In many industries there are regulations and regulations that require data storage and analysis in a specific time context. For example, in the financial sector, it is necessary to keep track of the time in which each transaction is made.
Many security and encryption protocols depend on timestamp accurate. For example, successful authentication of events or transactions may require precise time stamping. THE digital certificates eh token timed, are examples of how time is essential to ensure security in online transactions.
In distributed environments, such as microservizicoordinating transactions requires careful time management to ensure the consistency and integrity of operations.
NTP works in conjunction with satellite systems, such as GPS, and other technologies to synchronize the time across our many interconnected devices. The time taken from atomic clocks precise and aligned, it is for example transmitted via GPS to numerous receivers, including those in the towers mobile networks.
A project born from Dave Mills’ previous experiences
Engineer Mills had been working on ARPANET, the computer network for military use developed by DARPA, an agency of the US Department of Defense, from which the Internet that we all know was born. Already a professor in the 1970s at the University of Edinburgh, Mills had written programs that decoded short-wave radio and telegraph signals. Subsequently, mostly for fun, he studied as he did clocks of an electrical network could differ by several seconds due to the atmospheric temperature and the type of power supply (coal or hydroelectric energy).
Black magic for Vint Cerf that of Father Time of the Internet
By 1988, Mills had perfected how the protocol worked NTP to the point of being able to synchronize the clocks of computers connected to the network with an accuracy of a few tens of milliseconds. So much so that a Vint Cerfone of the “founding fathers” of the Internet and co-inventor of the TCP/IP protocol suite, whether it was “of some sort of black magic“. Cerf himself shared the news of the passing of the engineer, now known among his collaborators and beyond as the Father Time of the Internet.
Time synchronization that continues to evolve today
Beyond the incorrect implementations of NTP that have followed one another (one of the most recent being the failure to synchronize the Windows clock via Secure Time Seeding), as happens with practically any “piece of code”, over the years various problems also emerged in the various versions of the protocol. Since 2011, there have been several examples of DDoS attacks (Distributed Denial of Service) who used messages exchanged via NTP to block the normal functioning of other people’s services, rendered via the Internet.
Thus alternative implementations of NTP were also born. One of the most famous is NTPsec, designed to be more secure and resilient than the standard implementation. With a specific focus on security, NTPsec fixes vulnerabilities present in previous NTP implementations and pushes secure coding practices. It also seeks to promote clean, understandable, and maintainable code.
A company like Meta has announced that it has replaced NTP with PTP (Precision Time Protocol) to obtain time precision in the order of nanosecondi. Meanwhile, a group of around 20 experts formed within theInternet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the main Internet standards body, is working on NTPv5.
The fifth version of the protocol, however, could be quite different from the previous ones. Mills himself, rather embittered, declared that he no longer had “a say” as he once did. In any case, time synchronization on the Internet should be performed on rigorously tested code: and perhaps it is no coincidence that most systems today are still based on NTPv3, a release dating back to 1992.