Integrated graphics cards, otherwise called iGPU, are often an integral part of the processor. Although there are some models without integrated graphics card (or rather it’s there but it’s disabled), modern processors integrate basic graphics capabilities that are more than enough to handle your office work and multimedia needs.
The dedicated graphics cards are specifically designed to offer higher graphics performance. They are equipped with graphics processors (GPU) more powerful and more dedicated video memory. Integrated graphics cards, in fact, share the system memory with the CPU and are much less powerful.
A dedicated (or discrete) graphics card is suitable for performing complex graphics calculations due to the presence of a greater number of core CUDA o stream processor. They are therefore particularly suitable for game rendering, 3D graphics applications, video editing and other demanding tasks.
Is the integrated graphics card useless on systems equipped with a discrete video card?
On systems that use a dedicated graphics card, the presence of the iGPU may seem completely unnecessary. In reality, this setup brings gods with it anyway advantages.
When high graphics power is not needed, the integrated graphics card can handle basic graphics operations with a lower energy consumption compared to the dedicated graphics card. This can translate into longer battery life on portable devices such as commons notebook.
The integrated graphics card can also be used to manage theoutput video on secondary monitors. In this way, for example, it is possible to connect two monitors to the PC, reserving the use of the card dedicated to more graphically intensive applications.
Many integrated graphics cards still offer graphics capabilities hardware acceleration for the reproduction of multimedia contents: think of the decoding and encoding of high resolution videos.
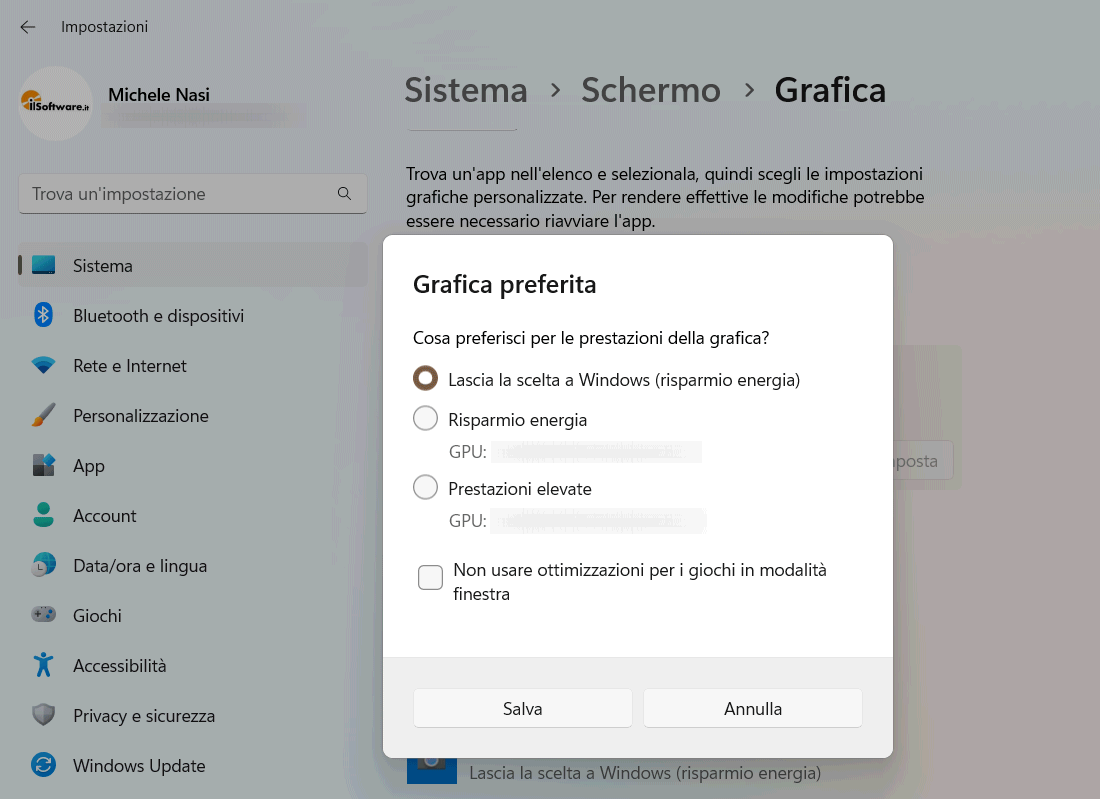
Already today it is possible to choose the graphics card to use in Windows and the same Windows 11 provides a renewed feature to define which GPU should use each application installed on the system. Just type Graphics settings in the operating system search box, press Enter, choose theapplication to configure Therefore Options.
The screen Favorite graphicsallows you to choose which video card to use for the selected application. By default, in fact, Windows 11 decides. Through the section Favorite graphicshowever, you have the ability to customize the setup and intelligently split workloads.
The role of the integrated graphics card becomes more important
As we have seen, Windows 11 timidly begins to offer some features to customize the behavior of the video cards installed on the system. In the future, however, the role of the integrated graphics card may become central. Even on systems with a particularly high hardware configuration.
When to use them applications which are largely based on GPU (video games but not only…) it happens that there is “down time”, with the performances that are negatively affected.
Take as an example the concept of preframe. In the graphic field, one of the most important elaborations has to do with establishing which objects are actually visible in each frame and which are not. This task is performed by the main GPU during the frame generation. For some time now, it has been used pre-renderingan approach which consists in generating not a frame with all the complete information, but an image as simple as possible to know which objects will be visible in the following frame.
What is pre-rendering
This is something that turns out to be easy to implement because the graphics driver only has to “sketch” the next frame in order to summarize its salient information and let the graphics card know what to do when it generates the final frame. Think about the pre-rendering like the sketch made by a draftsman before producing the complete work.
With the pre-rendering it comes completely discarded all geometry that is out of sight, behind a larger object, or too far away. To prepare the ground for the purposes of Ray Tracing, a tree structure indicates the location of each object. In addition, a rendering-based approach is set up “for tile“: By sorting the geometry based on its position on the screen, the impact on the usage of the is also reduced video memory.
Since only in the stages after the rasterization more data moves, and as a result, more graphics horsepower is needed, creating a preframe simplified you can work on much simpler hardware. Therefore, the card integrated in the processor returns to play an essential role.
What contains the preframe generated by the integrated board
The preframe built by the integrated board is something that will not be never visible on the screen. It omits some parts of the pipeline 3D to speed up construction. Graphic shaders, textures, color information, image post-processing effects are missing.
The idea is to generate the preframes in a few milliseconds, so that the information is ready in time to allow the GPU to use it to its advantage and generate the final frame even faster and more effectively.
With the proposed solution, discrete and integrated graphics would cooperate to deliver improved performance and optimized results. The fact is that the described solution could become accessible in practice only when the architecture of both GPUs is the same or at least is compatible.
This, unfortunately, is already a problem in itself: NVidiadifferently from Intel e AMD, does not have an x86 CPU with integrated graphics section. The preframe idea is ideal for GPUs with a large number of cores; however, as the cost of building chips gradually increases, any outside help is welcome.